Environmental data
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

The availability of user-friendly, high-resolution global environmental datasets is crucial for bioclimatic modelling. For terrestrial environments, WorldClim has served this purpose since 2005, but equivalent marine data only became available in 2012, with pioneer initiatives like Bio-ORACLE providing data layers for several ecologically relevant variables. Currently, the available marine data packages have not yet been updated to the most recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predictions nor to present times, and are mostly restricted to the top surface layer of the oceans, precluding the modelling of a large fraction of the benthic diversity that inhabits deeper habitats. To address this gap, we present a significant update of Bio-ORACLE for new future climate scenarios, present-day conditions and benthic layers (near sea bottom). The reliability of data layers was assessed using a cross-validation framework against in situ quality-controlled data. This test showed a generally good agreement between our data layers and the global climatic patterns. We also provide a package of functions in the R software environment (sdmpredictors) to facilitate listing, extraction and management of data layers and allow easy integration with the available pipelines for bioclimatic modelling.
-
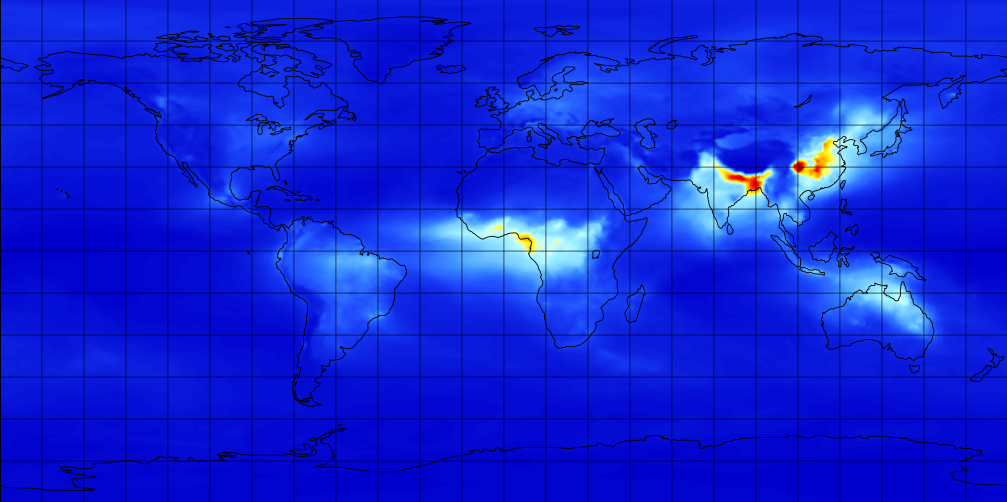
M2TMNXAER (or tavgM_2d_aer_Nx) is a time-averaged 2-dimensional monthly mean data collection in Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications version 2 (MERRA-2). This collection consists of assimilated aerosol diagnostics, such as column mass density of aerosol components (black carbon, dust, sea salt, sulfate, and organic carbon), surface mass concentration of aerosol components, and total extinction (and scattering ) aerosol optical thickness (AOT) at 550 nm. The total PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10 may be derived with the formula described in the FAQs under the Documentation tab of this page. The collection also includes variance of certain parameters. MERRA-2 is the latest version of global atmospheric reanalysis for the satellite era produced by NASA Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) using the Goddard Earth Observing System Model (GEOS) version 5.12.4. The dataset covers the period of 1980-present with the latency of ~3 weeks after the end of a month.
-

The Surface Ocean CO₂ Atlas (SOCAT) is a synthesis activity for quality-controlled, surface ocean fCO₂ (fugacity of carbon dioxide) observations by the international marine carbon research community (>100 contributors). SOCAT data is publicly available, discoverable and citable. SOCAT enables quantification of the ocean carbon sink and ocean acidification and evaluation of ocean biogeochemical models. SOCAT, which celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2017, represents a milestone in biogeochemical and climate research and in informing policy. SOCAT data are released in versions. Each succeeding version contains new data sets as well as updates of older ones. The first version of SOCAT was released in 2011, the second and third version followed biennially. Automation allowed annual public releases since version 4. The latest SOCAT version (version 2022) has 35.6 million observations from 1957 to 2022 for the global oceans and coastal seas. 7.2 million calibrated sensor observations are also available. SOCAT version 2023 was released on the 20th of June 2023, containing data submitted on or before 15th of January 2023. New data submissions are welcome at any time, and will be included in the next SOCAT release. The submission deadline for v2024 is 15 January 2024. SOCAT is a core Global Ocean Observing System data product for biogeochemistry endorsed by the Global Ocean Observing System GOOS.
-
Stakeholder networks from 32 countries united to collaborate on Ocean Action, Climate Action, addressing pollution from land-based, riverine and marine-based sources and advancing Circular Economy development. International Waste Platform provides international expertise and launches joint initiatives; It supports advancing solutions to mitigate the global waste, plastic pollution & climate crises which are interlinked. Representatives committed themselves to align objectives, to support the implementation of strategies of Ocean Action and Climate Action, as well as to share ideas, best practices, concepts, programs, knowledge and opportunities; including the reduction of plastic debris at the source, before it enters rivers and the coastal environment. Country / regional networks and national marine debris networks make a difference in societal behaviour change and environmental policies by providing input and promoting action which aims at finding solutions to reduce (ocean) plastic pollution. Country and regional networks are instrumental to reach the prevention and reduction of marine pollution, facilitate and foster the establishment of national and international partnerships in a multi-stakeholder approach.
-
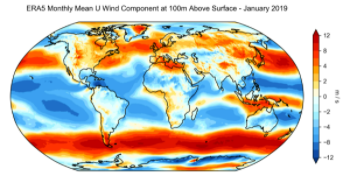
ERA5 is the fifth generation ECMWF reanalysis for the global climate and weather for the past 4 to 7 decades. Currently data is available from 1950, split into Climate Data Store entries for 1950-1978 (preliminary back extension) and from 1979 onwards (final release plus timely updates, this page). ERA5 replaces the ERA-Interim reanalysis. Reanalysis combines model data with observations from across the world into a globally complete and consistent dataset using the laws of physics. This principle, called data assimilation, is based on the method used by numerical weather prediction centres, where every so many hours (12 hours at ECMWF) a previous forecast is combined with newly available observations in an optimal way to produce a new best estimate of the state of the atmosphere, called analysis, from which an updated, improved forecast is issued. Reanalysis works in the same way, but at reduced resolution to allow for the provision of a dataset spanning back several decades. Reanalysis does not have the constraint of issuing timely forecasts, so there is more time to collect observations, and when going further back in time, to allow for the ingestion of improved versions of the original observations, which all benefit the quality of the reanalysis product. ERA5 provides hourly estimates for a large number of atmospheric, ocean-wave and land-surface quantities. An uncertainty estimate is sampled by an underlying 10-member ensemble at three-hourly intervals. Ensemble mean and spread have been pre-computed for convenience. Such uncertainty estimates are closely related to the information content of the available observing system which has evolved considerably over time. They also indicate flow-dependent sensitive areas. To facilitate many climate applications, monthly-mean averages have been pre-calculated too, though monthly means are not available for the ensemble mean and spread. ERA5 is updated daily with a latency of about 5 days (monthly means are available around the 6th of each month). In case that serious flaws are detected in this early release (called ERA5T), this data could be different from the final release 2 to 3 months later. So far this has not been the case and when this does occur users will be notified. The data set presented here is a regridded subset of the full ERA5 data set on native resolution. It is online on spinning disk, which should ensure fast and easy access. It should satisfy the requirements for most common applications. An overview of all ERA5 datasets can be found in this article. Information on access to ERA5 data on native resolution is provided in these guidelines. Data has been regridded to a regular lat-lon grid of 0.25 degrees for the reanalysis and 0.5 degrees for the uncertainty estimate (0.5 and 1 degree respectively for ocean waves). There are four main sub sets: hourly and monthly products, both on pressure levels (upper air fields) and single levels (atmospheric, ocean-wave and land surface quantities). The present entry is "ERA5 monthly mean data on single levels from 1979 to present".
-
Understanding how much inorganic fertilizer (referred to as fertilizer) is applied to different crops at national, regional and global levels is an essential component of fertilizer consumption analysis and demand projection. Good information on fertilizer use by crop (FUBC) is rarely available because it is difficult to collect and time-consuming to process and validate. To fill this gap, a first global FUBC report was published in 1992 for the 1990/1991 period, based on an expert survey conducted jointly by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the UN, the International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC) and the International Fertilizer Association (IFA). Since then, similar expert surveys have been carried out and published every two to four years in the main fertilizer-consuming countries. Since 2008 IFA has led these efforts and, to our knowledge, remains the only globally available data set on FUBC. This dataset includes data (in CSV format) from a survey carried out by IFA to represent the 2017–18 period as well as a collation of all historic FUBC data.
-
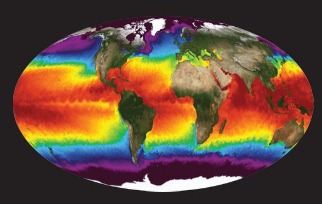
NASA's Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center (PO.DAAC) is located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. PO.DAAC manages and provides tools and services for NASA's oceanographic and hydrologic data (satellite, airborne, and in-situ) to enable a greater understanding of the physical processes and conditions of the global ocean. Measurements include gravity, ocean winds, sea surface temperature, ocean surface topography, sea surface salinity, and circulation. The data support a wide range of applications including climate research, weather prediction, resource management, policy, and the stewardship of ocean data resources.
-

Several climate indices, regarding Atlantic Basin: - North Atlantic Oscillation - Southern Oscillation Index - Bivariate ENSO Timeseries - Tropical Northern Atlantic Index - Tropical Southern Atlantic Index - Oceanic Niño Index - Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI V2) - North Tropical Atlantic SST Index - ENSO precipitation index - Northeast Brazil Rainfall Anomaly - Solar Flux (10.7cm) - Global Mean Lan/Ocean Temperature
-

Data and imagery from the Atlantic basin: - Climate - Cloud Profiling Radars - Air-Sea & Air-Land Fluxes - Wind Profiling Radars - Satellite - Local Weather and Climate PSL archives a wide range of data ranging from gridded climate datasets extending hundreds of years to real-time wind profiler data at a single location. The data or products derived from this data, organized by type, are available to scientists and the general public at the links in the website. The third-party data appearing on this web site may be reformatted from their original form, but not altered as to the informational content contained therein. It is provided as a public service. Further, this data does not reflect an official view or position of NOAA.
-
Every year, millions of tons of plastic enter the oceans, of which the majority spills out from rivers. A portion of this plastic travels to ocean garbage patches, where it gets caught in a vortex of circulating currents alongside plastic from other sources (e.g. offshore fishing activities). If no action is taken, plastic will increasingly impact our ecosystems, health, and economies. The Ocean Cleanup is a non-profit organization developing and scaling technologies to rid the oceans of plastic. To achieve this objective, we have to work on a combination of closing the sources of plastic pollution and cleaning up what has already accumulated in the ocean and doesn’t go away by itself. This goal means we plan to put ourselves out of business – once we have completed this project, our work is done. To rid the oceans of plastic, we need not only to clean up what is already out there but also stop new plastic from entering the ocean – we need to close the tap. Working together with government leaders, individuals, and private corporations, our goal is to tackle these 1000 most polluting rivers all over the world Every single year, marine plastic costs the economy (6 to 19) billions of dollars – impacting tourism, fisheries and aquaculture, and (governmental) cleanups. And that doesn’t include the impact on our health and on the marine ecosystem. Intercepting plastic in rivers is much more cost-effective than dealing with the consequences downstream.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA